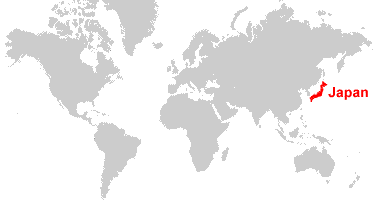
Japan is a nation located in the eastern Pacific Ocean. It has an area of 145,847 sq km and extends over the eight major islands of Hokkaido, Honshu, Kyushu, Shikoku, and some 4,000 small islands. The population is 127 million. The official language is Japanese; there are no indigenous languages. Tokyo’s capital and other large cities are Nagoya, Osaka, Kobe, and Yokohama. The three largest islands (Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu) are connected by railways and highways. Japan has a highly developed capitalist economy with a GDP of $4.9 trillion in 2013 (Wikipedia).
Japan is a resource-poor country, but it has two primary natural resources: a prosperous fishing industry in the North Pacific and rich mineral deposits such as gold, silver, copper, and coal in the south.
What Hemisphere is Japan in?
Japan is located in both the northern and eastern hemispheres because its latitude is 36.2048° N, and its longitude is 138.2529° E.
Satellite photos show that Japan consists of two parts separated by the Sea of Japan: the northern part, which includes Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu, features numerous mountain ranges. The island areas are covered with dense forests, while the middle and southern parts are mainly composed of flat plains or gently rolling hills. The climate varies from temperate in the north to subtropical in the south; there are four seasons. The highest mountain is Mount Fuji, at 3,776m.
Is Japan in the Northern Hemisphere?
Japan is in the Northern Hemisphere because its latitude is 36.2048° N.
Is Japan in the eastern or western Hemisphere?
Japan is located in the eastern Hemisphere because the country’s longitude is 138.2529° E.
What is the latitude of Tokyo, Japan?
Tokyo’s latitude is 35.652832 degrees, and its longitude is 139.839478 degrees. The city is located on the southeastern side of Japan’s main island, Honshu, on the coast of Tokyo Bay in the Pacific Ocean.
Most Extreme Points of Japan in Four Cardinal Directions
Japan’s northernmost latitude is 45.31 ° N. The most extreme point is the top of Mount Hakutetsu, at 1,960 m.
In the east-south part, Japan reaches a longitude of 138.2529 E. The most extreme point in that direction is the top of Mount Hakutetsu at 1,960 m.
In the southwest part of Japan, Japan reaches a latitude of 37.21′ S. The most extreme point in that direction is the top of Mount Hakutetsu at 1,960 m.
Japan reaches a longitude of 138.2529 E in the west-north. The most extreme point in that direction is the top of Mount Hakutetsu, at 1,960 m.
Japan reaches a latitude of 30.33′ N in the west-north part. The most extreme point in that direction is the top of Mount Hakutetsu, at 1,960 m.
The farthest point from the sea (1860 m) is at the top of Mount Hakutetsu. The most distant point from the sea in an easterly direction (2,235 m) is Mount Tenji. The farthest point from the sea in a southerly direction (1,190 m) is at Mount Kaimon. The most distant point from the sea in a westerly direction (820 m) is Mount Tateshina. The farthest point from the sea in an easterly direction (720 m) is at Mount Kakinohana. The most distant point from the sea in a westerly direction (520 m) is Mount Terashima.
The most extended mountain range is 4,210 km, the most extended plateau is 1,320 km, the most considerable valley is 960 km, and the most profound canyon is 685 m.
The world is divided into six climate zones: temperate and torrid, cool and cold, and five tundra zones. There are four seasons: winter, spring, summer, and autumn. Japan’s climate is temperate in the north and subtropical in the south; it has four main seasons. The most temperate region is in the north; the average temperature in January is -0.5, and the average in July is 19.2.
What is a Map of Japan?
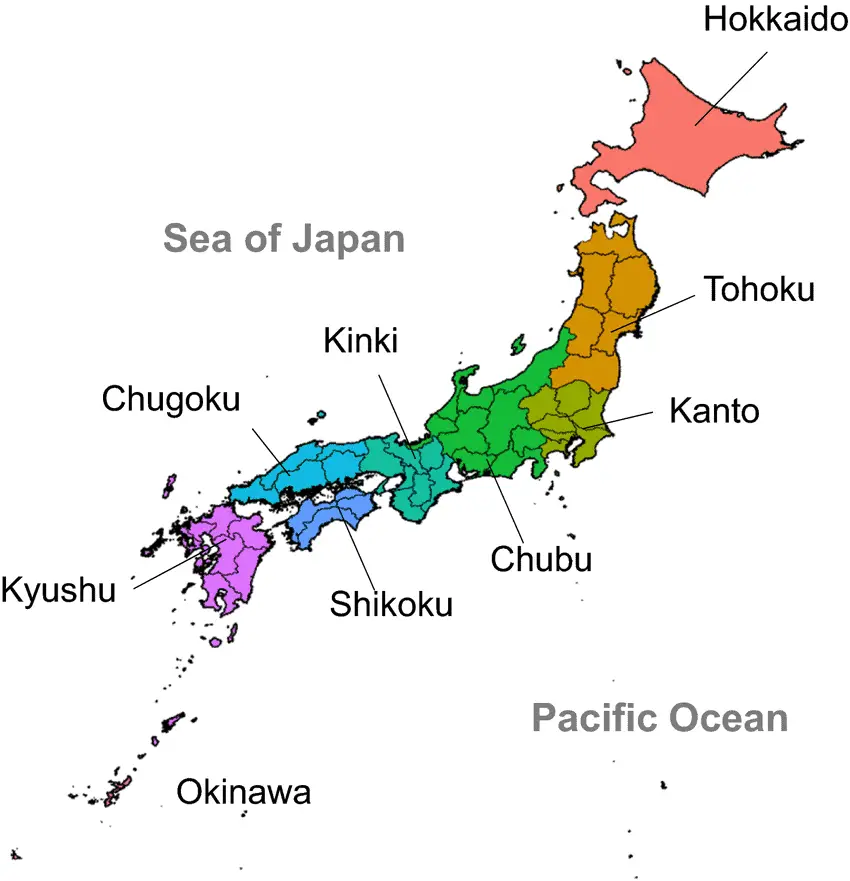
A map of Japan includes two main parts: The main islands and areas surrounding it, such as Russia, South Korea, China, etc.
Japan has four major islands (Hokkaido, Honshu, Kyushu, and Shikoku) connected by railways and highways, as well as many smaller islands.
The four main islands (Hokkaido, Honshu, Kyushu, and Shikoku) are located in two main geometrical areas: Hokkaido and Western Honshu, Kyushu and Eastern Honshu. In the northern part of Japan, the latitude is 4531′ N; in the south, it is 3719′ S. The distance from Hokkaido to Tokyo is 550 km.
Conclusion
Japan’s location influences its culture, history, politics, and economics. It is a resource-poor country, but it has two primary natural resources: a prosperous fishing industry in the North Pacific and rich mineral deposits such as gold, silver, copper, and coal in the south.
- 6 Proven Ways SaaS Founders Actually Get Customers (With Real Examples) - December 17, 2025
- Facebook Ads to Get Followers! - December 27, 2024
- ClickUp vs. Slack - December 20, 2024