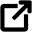Netlogon is an essential component of the Microsoft Windows operating system. It authenticates users, computers, and services in a Windows domain environment. It is also responsible for providing secure authentication and authorization services from a centralized server to each client in the network.
Netlogon has existed since Windows NT 4.0. However, its role has grown significantly since the introduction of Active Directory in Windows 2000. Netlogon establishes a secure channel between an authentication client (such as a Windows computer) and the domain controller (DC). The DC validates user credentials before allowing access to resources such as printers and file shares. The secure channel also helps protect credentials by encrypting them as they’re sent across the wire from the client to the server.
In addition to user authentication, Netlogon is also used for other connections such as Group Policy processing, remote procedure calls (RPC), computer name registration, time synchronization, and more. Netlogon uses UDP port 138 for broadcast requests and TCP port 139 for client-server communications. Additionally, it can use UDP ports 137 and 445 when communicating with older systems that do not support RPC over TCP/IP.
Netlogon employs several security protocols, such as the Kerberos v5 protocol and Secure Remote Password Protocol (SRP), to ensure that communication between clients and servers remains secure. Kerberos provides mutual authentication between clients and servers, while SRP offers additional protection against dictionary attacks on weak passwords. To further secure data transmitted over the wire, Netlogon also supports encryption algorithms such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) 128-bit or 256-bit encryption with Secure Socket Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS).
What is NetLogon? How does NetLogon work?
NetLogon represents a Windows Server authentication process (Windows service) responsible for creating a secure channel between computers and domain controllers. In the Windows Client Authentication Architecture, NetLogon verifies login requests and authenticates users and other services within a domain.
Now let us see the Netlogon folder location on my Windows system:
Where is the Netlogon folder?
The NetLogon folder is located in the following path: %systemroot%\Sysvol\Sysvol\Domain Name\Scripts. The NetLogon folder is a shared folder that contains the group policy logon script files and other executable files. Netlogon share location is in the folder Scripts, not NETLOGON (%systemroot%\Sysvol\Sysvol\Domain Name\Scripts).
How to find the Netlogon folder if you can not find a Sysvol folder:
Please go to the Registry Editor if you can not find the Netlogon folder.
- Click Start, click Run, type Regedit, and then click OK.
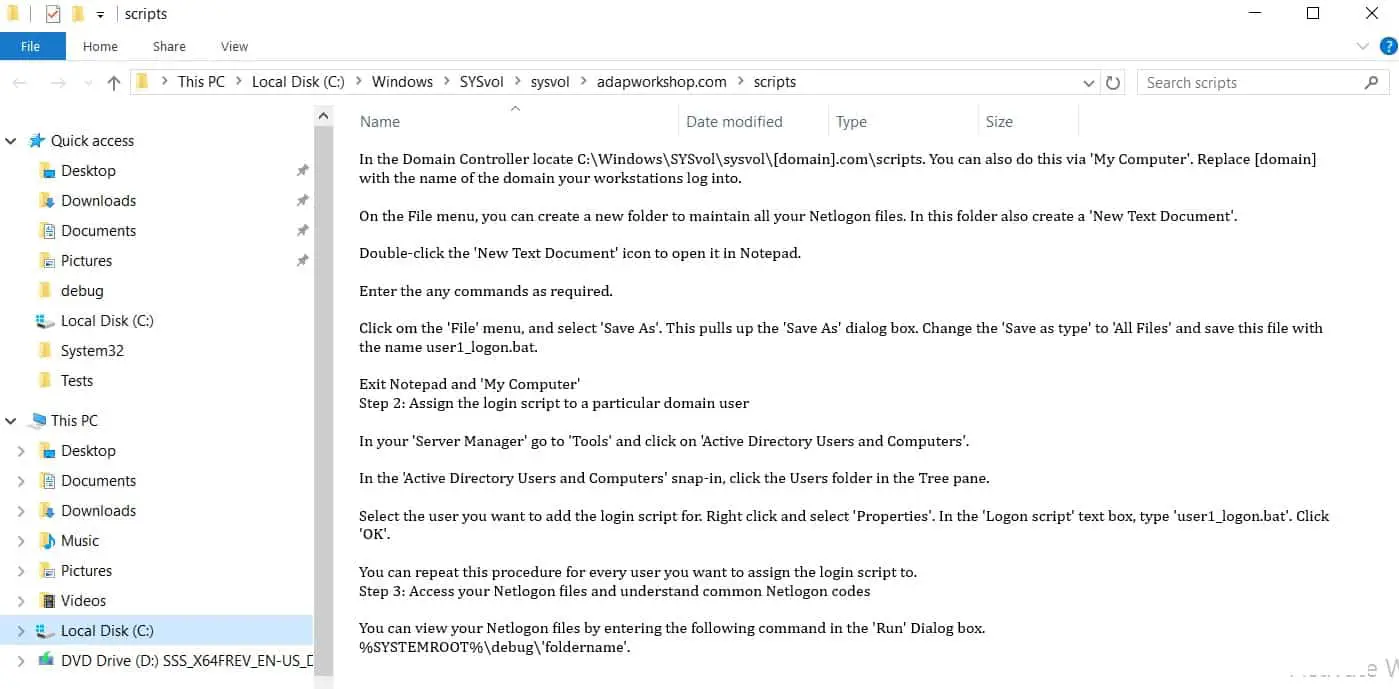
- Locate the following subkey in Registry Editor: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Netlogon\Parameters
Here in Registry Editor, you will see the Netlogon Folder path.
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Netlogon:
Can the NetLogon be stopped from running in the background?
Yes, NetLogon can be stopped from running in the background. Nonetheless, one has to do it manually or by a runtime error. Go to the Command Line ( Terminal) to stop or restart it. Users must remember that preventing the NetLogon can hamper many Windows Server functions.
How do you enable the Netlogon logging server 2008 or any Windows?
To enable NetLogon logging, run the following command (from an elevated command prompt): nltest /dbflag:0x2080ffff. Then, you need to stop and restart the logging service, either visually using services.MSC command or using command prompt:
nltest /dbflag:0x2080ffff
net stop netlogon
How to start the NetLogon service?
To start the NetLogon service, use Start run services. msc. Then, choose the Services Desktop app. Click Netlogon, and then click Automatic in the Startup type box.
When does NetLogon start operating in the background?
NetLogon starts running in the background only after the Workstation starts its function.
Did you know that as you use your PC/ laptop, NetLogon keeps running in the background?
NetLogon Example:
Domain Controller will fail to register the names of the domains in the records. Since the records contain user login information, you can no longer log in to your accounts.
Conclusion
In my opinion, the Netlogon folder is very fast to find if you use Regedit (Registry Editor). The full path to the desired folder will be stored.
Overall, Netlogon plays a critical role in any Windows environment where secure authentication and authorization are required, as it helps ensure that only authenticated users have access to sensitive resources on the network while keeping their credentials safe from external threats like hackers or malware attacks. Administrators can further increase security by enabling features like NAP, which checks whether clients comply with company policies before granting them access to network resources, thus helping maintain security standards within their organization’s IT infrastructure.
- Facebook Ads to Get Followers! - December 27, 2024
- ClickUp vs. Slack - December 20, 2024
- Mastering E-Commerce Analytics: A Blueprint for Success