What is mSATA SSD?
mSATA SSD or Mini SATA represents a small form solid-state drive. They have no moving parts and use flash memory. These small-form flash drives are applied in space-constrained devices such as laptops, netbooks, and tablets.
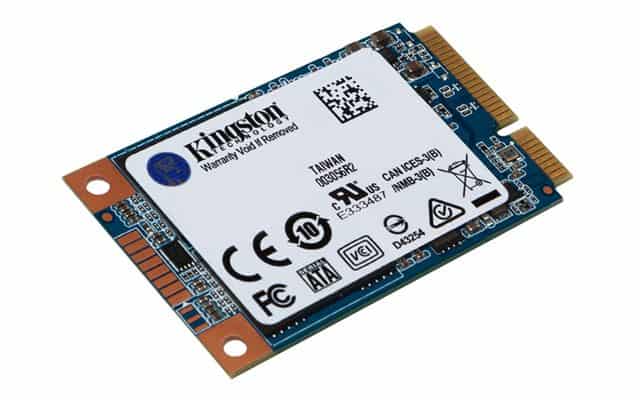

mSATA or mini-SATA for its abbreviation mini Serial Advanced Technology Attachment is a bus interface used in computers to transfer data between the motherboard, and the storage elements that are contacted through this interface, the devices that can be connected are small solid disks with a maximum throughput of 6 Gbit per second. The mSATA connector is similar or practically identical to M.2, but they are incompatible since each uses a specific controller; thus, mSATA uses an S-ATA host controller and M.2 a PCI-express.
Although SATA dates from 2001 in its first version, mSATA saw the light in 2009 to use smaller units than hard drives or 3.5″ 2.5″ “SDs and are typically connected directly to the motherboard with a screw and this connector. The mSATA interface was looking for speed when transferring data in a small space but was limited to the SATA III bandwidth of 6 Gbits per second; however, its successor, the NVMe format, has been achieved through a PCI controller to get much more bandwidth in storage devices, up to 7000 MBps reach the SSD 980 Pro from Samsung.
The mSATA interface is currently in disuse in desktop PCs and laptops since its transfer speed is limited to SATA III, 6 Gbits per second. Connecting an SSD to a SATA connector III standard would be the same as having an SSD connected to a SATA connector III standard, and they are usually cheaper if they are recommended when the problem is the space available to install 2.5 “oor 3.5” “iISKssince these mSATA disks take up much less space.
An mSATA SSD is generally the size of a business card. Its benefits include a small structure factor, low force utilization, stun/vibration resistance, and quick boot/closure capacities. The maximum transmission capacity of an mSATA SSD is 6 gigabits each second (Gbps).
Is mSATA obsolete?
Yes, mSATA is obsolete because M.2 SSDs are several times faster than mSATA; they are ultra-thin and plugged directly into the motherboard using a dedicated M.2 connector slot.
M.2 SSD vs. mSATA SSD
Differences between M.2 SSD and mSATA are:
- While SATA drives have a maximum speed of 600 MB per second, M. 2 PCIe cards have a maximum speed of 4 GB per second.
- SATA SSDs are connected to the motherboard via cable, while M.2 SSDs are plugged directly into the motherboard using a dedicated M.2 connector slot.
- SATA is typically 4 inches wide, 1.03 inches tall, and 5.79 inches long, while M.2 SSD is ultra-thin (several millimeters).
You can read more about M.2 SSD  in our article.
in our article.
- Facebook Ads to Get Followers! - December 27, 2024
- ClickUp vs. Slack - December 20, 2024
- Mastering E-Commerce Analytics: A Blueprint for Success


