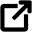Apt-get is a powerful command-line tool to manage and perform complex package operations. With apt-get, you can install, update, and remove packages from your system, browse the available packages, and view detailed information about them. To use apt-get, open a terminal window and run the command apt-get followed by the desired operation. For example, to install a new package on your Linux system, you might run the command:
apt-get install
This will download and install the specified package and any dependencies it may have. Similarly, by selecting the appropriate options, you can use apt-get to update or remove existing packages from your system. Overall, apt-get is a potent tool for managing packages on your Linux system, making it easy to keep all your software up-to-date and easily uninstall any software you no longer need.
However, in MAC, you need to find another alternative for apt-get.
How to Install APT-GET on Mac?
If you want to install apt-get on Mac or YUM, try the sdkman.io tool. It will enable the management of parallel versions of multiple software development kits and offer an excellent CLI. Additionally, you can use some other command-line tools on macOS, such as Homebrew and MacPorts.
Solutions are:
- Homebrew: http://brew.sh
- Macports: http://www.macports.org
- SDKman https://sdkman.io/
Homebrew
Before you can install Homebrew, Homebrew the system requirements for your operating system.
On macOS: You will need the latest version and an internet connection to install Homebrew. HomHomebrewy, you will need administrative privileges on your computer to install Homebrew.
Homebrewstalls the package available.
To install Homebrew, visit the official homepage and watch the installation script. Once the download is complete, run the script to begin the installation process.
Next, follow any on-screen prompts or instructions while Homebrew homeHomebrewn your computer. Once the installation is complete, you can use Homebrew homebrew packages and other software on your computer.
Now that you know how to install Homebrew on your Home computer, you can easily manage and update your software packages and other tools. With just a few simple commands, you can download and install new software packages from hundreds of different repositories online, making it easy to customize your computer to suit your needs.
macOS Requirements
- A 64-bit Intel CPU or Apple Silicon CPU
- macOS Big Sur (11) (or higher)
- Command Line Tools (CLT) for Xcode (from
xcode-select --install
or https://developer.apple.com/download/all/) or Xcode 3
- The Bourne-again shell for installation (i.e.
bash
)
Install Macports
To install Macports on your Mac, you must first have Xcode and the Xcode Command Line Tools installed. Once you have these tools set up, open a terminal and enter the following command to agree to the Xcode license:
Sudo xcodebuild -license
Next, you will need to download and install the latest MacPorts version for your specific Mac OS. Instructions for this can be found on the official MacPorts website.
Once MacPorts is installed, you can easily compile, install, and upgrade any open-source software packages on your Mac. To do so, open a terminal and enter the following command:
sudo port <package name>
More detailed installation instructions and documentation are on the official MacPorts website. With just a few simple commands, you can use thousands of free, open-source software packages available for your Mac using MacPorts.
Can I install YUM on Mac as an Alternative?
You can not directly install YUM on a Mac. However, you can try installing kman.io, Homebrew, and Homesites, which are excellent alternatives.
YUM, or the Yellowdog Updater, Modified, is a powerful package management tool for managing software packages on your Linux system. With YUM, you can install, update, and uninstall packages quickly and easily, as well as manage package dependencies to ensure your software is up-to-date and functioning correctly.
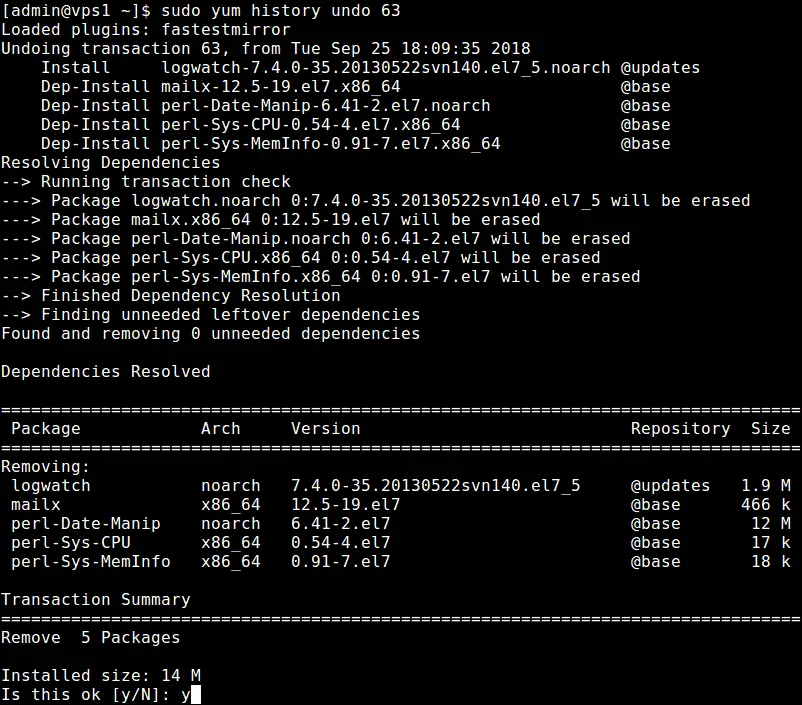
To start with YUM, open up your terminal program and type in the command yum. This will include a list of all the basic commands you can use with YUM. Some of the most common commands include installing new packages, updating existing packages, searching for packages by name or description, uninstalling packages, and managing dependencies.
There are also several tools available that provide graphical interfaces to YUM functionality. These tools can make it even easier to manage your software packages using YUM and help you take full advantage of all its features. With YUM, you can stay up-to-date and function smoothly on your Linux system.
- 6 Proven Ways SaaS Founders Actually Get Customers (With Real Examples) - December 17, 2025
- Facebook Ads to Get Followers! - December 27, 2024
- ClickUp vs. Slack - December 20, 2024