Netlogon Logging can be a valuable tool for IT professionals to help troubleshoot networking issues. It captures events such as computer authentication and user logins and provides an audit trail that can help isolate issues. This article will illustrate how to enable Netlogon logging on Windows systems.
The first two steps you can use to find the Netlogon folder (read more in our article)
Please go to the Registry Editor if you can not find the Netlogon folder.
- Click Start, click Run, type Regedit, and then click OK.
- Locate the following subkey in Registry Editor: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Netlogon\Parameters
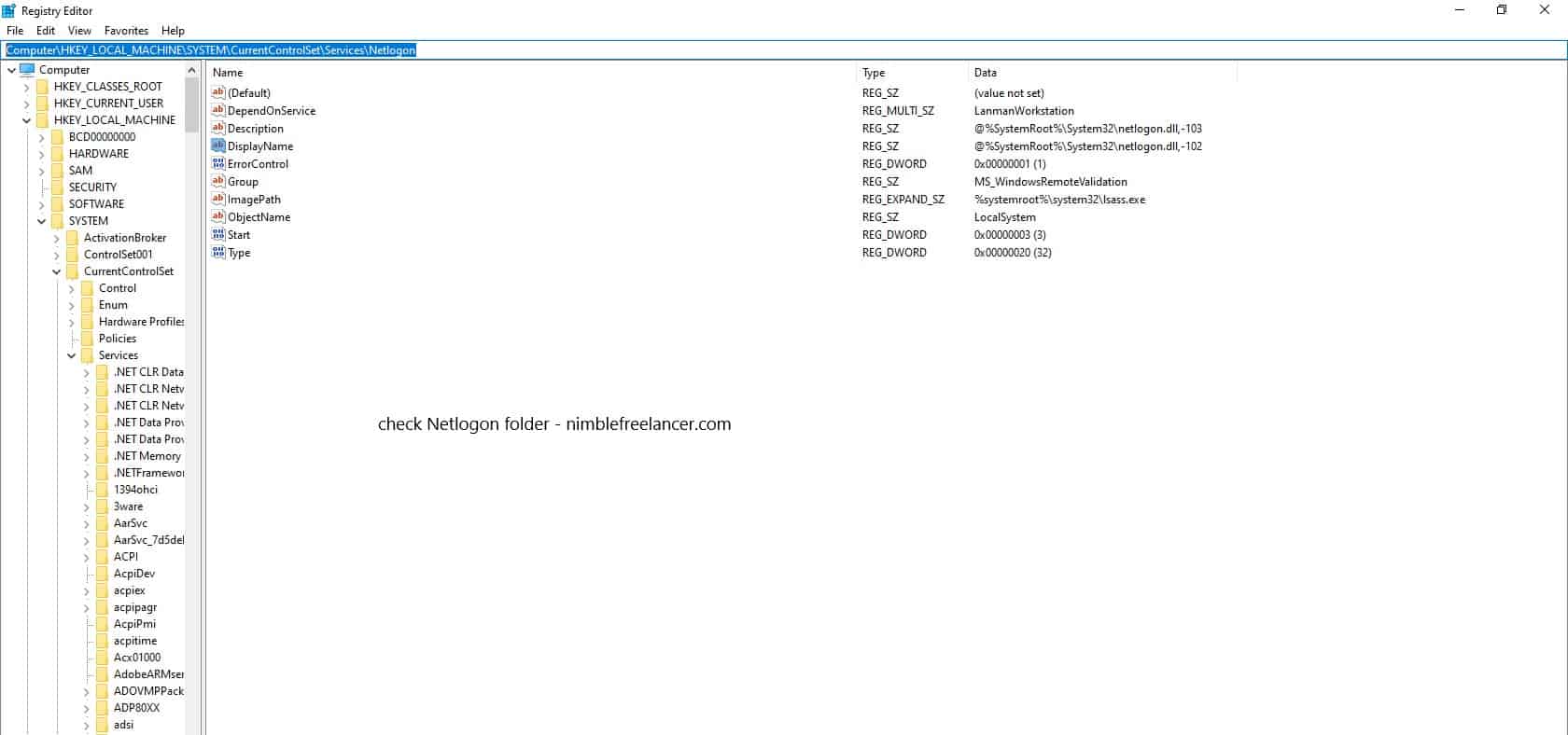
- In the details pane of the Registry editor window, right-click on the “SysvolReady flag” and choose Modify from the context menu that appears.
- In the Value data box, enter 0 (zero) and click OK. This will set up NetLogon logging for errors and warnings by default.
- Again, in the details pane, right-click on the SysvolReady flag, select Modify from the context menu that appears, and enter a value of 1 (one) into the Value data box before clicking OK to confirm your changes.
- To enable logging for all events (e.g., successes and errors/warnings), right-click on NetLogon again in Registry Editor’s left pane and choose New > DWORD Value from its context menu.
- Name this new DWORD LogLevel and give it a value of 5 (five). This will turn on verbose logging for all events related to NetLogon operations – i.e., successes and any errors or warnings encountered – allowing you to investigate further, if necessary when attempting to troubleshoot any issues with your network logins or authentication processes.
- Finally, restart your computer for these changes to take effect before attempting any additional logins or authentication processes; this will ensure that your new settings have been applied correctly and are appropriately used for your network operations.
Enabling Netlogon logging is a two-step process. The first step involves opening the Registry Editor and deleting any existing Reg_SZ values for the DBFlag entry under the key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Netlogon\Parameters and replacing it with a REG_DWORD value of 2080FFFF hexadecimal value. To do this, open the Start menu, click Run, type Regedit into the text field, and click OK. Navigate to the appropriate registry key, delete existing values, or create a new DWORD value if necessary. Once you have added the new DWORD value, save your changes and close the Registry Editor.
The second step in enabling Netlogon logging is to set the DBFlag data value in the Registry Editor to 0x0. To do this, open the Start menu again, click Run, type Regedit into the text field again, and then click OK. Locate HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesNetlogonParametersDBFlag in the Registry Editor and change its data value to 0x0. Save your changes and exit the Registry Editor once more.
Now, Netlogon logging should be enabled on your Windows system. Whenever an event related to Netlogon occurs (such as a login or authentication attempt), it will be logged in Event Viewer under Applications And Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > Netlogon > Operational log. This can be accessed through Computer Management (Local) in Server Manager on Windows Server machines or by searching for Event Viewer in Control Panel on client machines running Windows 10 or 7 (or 8/8.1). You can also use PowerShell commands such as Get-EventLog -Logname “Microsoft-Windows-NetLogon/Operational” -Newest 10 to view recent events captured by Netlogon Logging without going through Event Viewer directly.
You should now have a basic understanding of how to enable Netlogon logging on Windows systems; however, there are other essential considerations you should keep in mind when working with this feature:
• It is recommended that you audit any events found within these logs regularly for suspicious activity, such as failed logins or unauthorized access attempts
• Be aware that enabling high levels of detail when using Netlogon Logging can lead to increased disk usage, which could affect system performance if not monitored carefully
• When possible, try using Group Policy settings instead of manually modifying registry keys whenever possible
By following these steps correctly, you should now have enabled successful Netlogon logging on your Windows systems; however, you must never forget good security practices when dealing with sensitive information, such as network authentication logs, so that they remain safe from malicious actors attempting unauthorized access attempts!
- Facebook Ads to Get Followers! - December 27, 2024
- ClickUp vs. Slack - December 20, 2024
- Mastering E-Commerce Analytics: A Blueprint for Success