To start work in your backyard, you must know about building permits and codes to build an innovative workspace. When constructing anything on a base, it’s critical to understand the depths at which the frost line is located to avoid structural damage initiated by the frost heave.
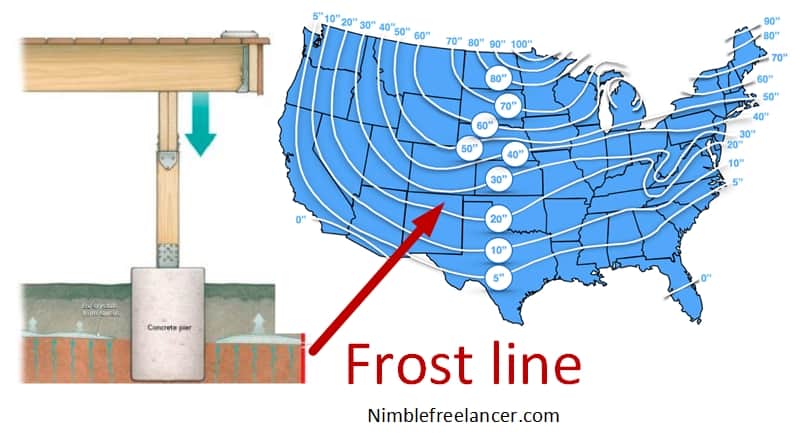
A frost line is worldwide, but the depth of that frost line varies from place to place. In addition to soil type, humidity content, and ordinary temperatures, these factors affect the frost line. Before starting a project, ensure you know how deep the frost line needs to be in your area according to the local building codes. Make sure you have enough substantial and that footings are firmly mounted in the ground beneath the frost line by planning out your project in advance.
To start digging, you usually need to know the average depth at which the ground freezes yearly. In that case, in our article, you must check the frost line depth using the zip code.
How to Check Frost Depth?
To check frost depth, you need to use the Frost Tube instrument. The main idea in checking frost depth is to put some volume of water with numerical measurement indicators into the Frost Tube and determine the frost depth based on the line at which the water freezes. The innermost Frost Tube is a piece of clear tubing sealed on both ends, which holds colored water, while the outer tube is a piece of PVC pipe filled with a PVC end plug secured with cement on the bottom fitted with a removable cap on top. (see image).
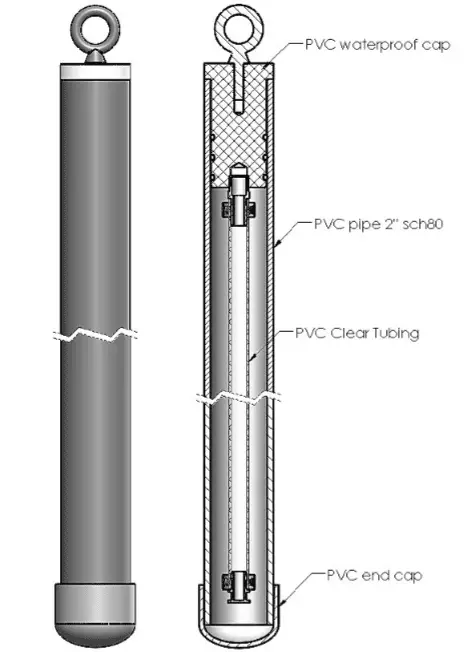
Below is presented Frost Tube in the fields that measure frost line depth:

When frost penetrates the ground and Frost Tube is in the ground, separation occurs between the water solution and blue methylene in a tube. The water solution becomes colorless when it is frozen. Blue methylene tends to remain in the unfrozen section of the tube because of its low density, where the concentrated solution is. This phenomenon is also reversible, which means it can follow the frost and thaw evolution over time.
However, engineers can not measure each inch of the Earth precisely and find the depth in the field. Because of that, engineers made unique frost line maps.
Main facts about maps:
- The depth below groundwater freezes is known as the “frost line.”
To fully appreciate the dangers of building or constructing other structures, one must grasp the frost line and how to measure its depth. Floras and faunas rely on moisture in the soil to survive and thrive, but when the weather turns cold, the groundwater freezes and expands, brashly devastating anything in its path.
Humidity, topsoil content, and regional average temperatures often determine where the frost line will appear. Frost tubes containing a minor hollow duct implanted into a punctured hole in the frozen ground are used to measure the exact depth. The stripe at which the water freezes is used to determine the depth of the tube using a bag of water containing measurement indicators. If unsure of the proper depth for your footings, check with your confined structure inspector or department.
- The depth of the frost line varies significantly across the country.
Because the weather varies so widely across the country, it stands to reason that the frost line depths in colder regions would differ from those in warmer areas. You should check your confined structure codes and frost line depth plots to know exactly how deep you should dig for top deck grips, barrier boundary markers, and bases.
The NWS (National Weather Service) offers a nationwide service. Enter your address or zip code to access a map of frost line depths for accurate, up-to-date information about the current frost level in your area. It’s essential to remember that this map is only for reference and shows the current depth of frost, so if it’s tested in midsummer, most locations won’t have any ice on them. The average maximum frost line for the area can be seen on many frost line depth maps.
- Damage to foundations, feet, and other structural elements can result from frost heave.
Frost heaves are a type of structural movement that can cause significant damage to buildings if markers, bases, balances, or other supports are fixed overhead the frost line. The formation of frost lenses in the ground causes the ground to rise when groundwater freezes and expands. As it grows, this lens forces dust, rocks, and other substances aloft, where they can be seen. There is a disorderly and powerful movement of compacted earth thEarths thEarthential to deform posts, shatter rock, and move the foundations of entire buildings.
Right afterward, the frosted lens has melted, and the dirt has returned to its original point; the arrangement will probably still be damaged and out of balance. By positioning essential maintenance at a depth of at least 2ft underneath the max frost depth, it is possible to reduce the likelihood that the structure will be forced upward and out of its intended location.
- Frost depth necessities are commonly included in building codes.
There are various sources to consult when determining where the ordinary frost line is in a given state, region, or city. Still, local building codes should always be the primary source of information for construction projects. Keeping these regulations up to date is a top priority for the area’s construction professionals so that marketable, manufacturing and uptown assembly adhere to the security limitations imposed by the local and state governments.
Checking the depth of the frost line shouldn’t be a problem because most construction projects require a construction license. Consult the government’s website to learn about local building regulations or ask for information when applying for a permit.
- Certain developments may necessitate consideration of the depth of the lateral frost line.
The best time to determine the local frost line depth is during a project’s planning phase and considering its impact on a structure. When constructing a gazebo for your courtyard or floor, which is a temporary structure, the frost line is not something that needs to be considered. However, when planning projects that rely on concrete foundations, it is essential to consider the depth of the frost line.
Think about how the depth of the frost line will influence your plans if you want to build a deck, fence, retentive partition, or even pour the base intended for a workspace. This is important to do to avoid any unpleasant surprises. Frost heaves can cause splintered floors, fragmented boundary markers, and insecure surfaces if maintenance is not mounted underneath the frost line to avoid substantial movement throughout the wintertime.