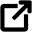So, as a freelancer, you need to use the Internet from your cable provider. You need to buy a router to understand wireless and the main terms of telecommunication.
Please visit the free online Wireless Networking course to learn more about wireless access points.
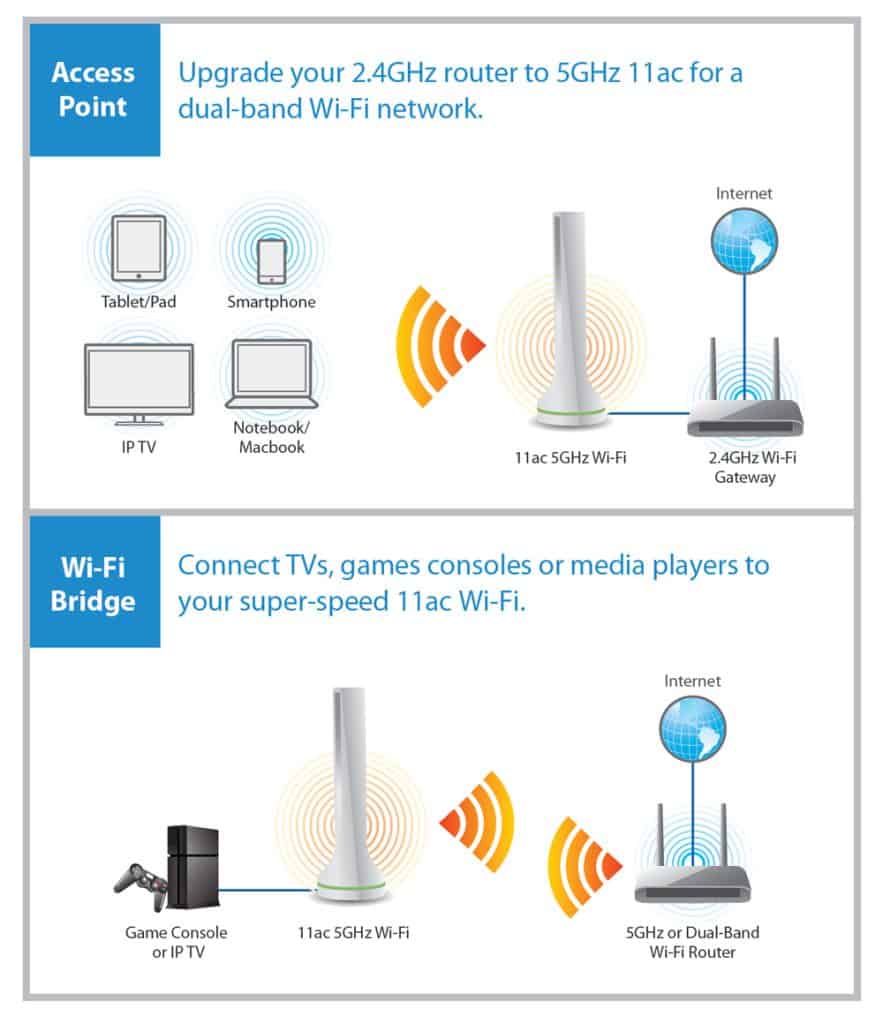
What is a wireless access point?
An access point is a device that creates WLAN, a wireless local area network. Usually, WLAN is in an office or large building. An access point connects to a wired router, switch, or hub via an Ethernet cable and projects a Wi-Fi signal to a designated area.
See more about wireless access points in this video below:
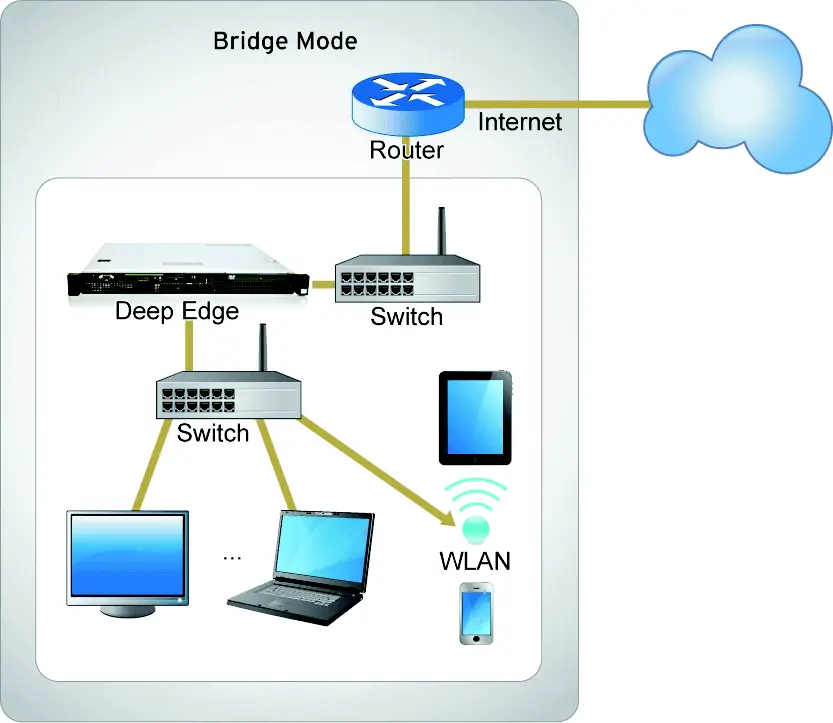
What is bridge mode in networking?
Bridge mode is a configuration that can connect multiple routers and extend Wi-Fi coverage in your office or home. It fixes this by letting multiple routers share one single Wi-Fi network. In addition, it disables the modem’s NAT feature and allows a router to function as a DHCP server without an IP Address conflict.
See this video for more details:
How do you set up a router in bridge mode?
- Reset your router to factory settings.
- Write down your primary router’s wireless settings, the Subnet Mask, and the IP number.
- Access the router’s interface.
- Choose the Bridge Mode
- If you can, choose the IP address of the old router or accept the new IP.
- Set up Wireless Settings, or you can skip this.
Router Bridge Mode vs. Access Point
The difference between router bridge mode and the wireless access point is in the systems they connect. A wireless access point connects users to a network by creating a wireless signal. In contrast, a router bridge mode connects separate networks, such as a wireless home network, to all devices connected to the bridge.
Remote Bridges
A PC network will generally be partitioned into different fragments that should be coordinated. For example, an organization connects interfaces such as separated organization sections, encouraging information sharing. Before Wi-Fi innovation, network spans were associated with wired ethernet links. In particular, in the OSI model setting, the network spans associate portions on layer 2 (information connect layer).
These are savvy gadgets contrasted with center points and repeaters that control the information stream forward and backward from the associated network portions. A remote bridge plays out a similar capacity of connecting network portions, yet it does that through a Wi-Fi interface rather than a wired ethernet connection. It can associate two organizations with a radio connection to encourage availability and information move between them.
Such scaffolds may likewise be utilized to associate an ethernet organization with a point or remote switch for Internet availability. Using a ‘Remote Distribution System,’ spans are set up to interface various organizations. There is more than one sort of remote scaffold, going from essential ones, which encourage ethernet availability with a distant point way, to ones that bend over as a distant point way and a bridge. That is, by all accounts, the wellspring of disarray between the two gadgets.
Remote Access Points
Remote point ways give Internet access by interfacing remote gadgets with switches. Thus, they go about as extenders of a Wi-Fi organization by straightforwardly giving Internet access over significant distances. Famously known as ‘Remote Hotspots,’ they are probably the most generally utilized systems administration instruments. A remote point provides Internet and LAN access to various gadgets.
Access Point and Bridge Mode advanced knowledge.
Macintosh spans hand-off Layer 2 edges between LANs. For example, an Ethernet connect transfer outlines between two 802.3 LANs, while a remote scaffold transfer outlines between an 802.11 WLAN and an 802.3 LAN.
Most remote point ways (APS) work in “root mode” – a highlight multipoint arrangement in which the AP transfers outlines between numerous 802.11 stations and an adjoining Ethernet LAN.
Some APs can likewise work in “connect mode” – a highlight point arrangement in which the AP transfers outlines from one other 802.11 scaffold onto an adjoining Ethernet LAN.
Gadgets that are sold as remote bridges are intended to work (basically) in connect mode. For instance, remote outside scaffolds are regularly sent two by two to associate structure organizations, utilizing remote for the between-building jump.
In synopsis: Purchase an AP to associate numerous remote hosts with an organization, yet buy a remote bridge if you need to interface with wired organizations.
A point associated with your home organization with an Ethernet link makes another circle of remote inclusion, letting you add remote gadgets to your home organization. Pointways can add remote abilities to a non-remote switch or improve a remote organization’s speed and scope. When gadgets interface with your SSID, they join your prior wired LAN.
To stay away from disarray, fight the temptation to call this connecting. (While a point way may seem to connect the association between remote gadgets and an organization, it’s not interfacing separate organizations.) The qualification is significant: A remote point is a way to associate clients with an organization by making a remote sign they can utilize. Conversely, a bridge interfaces separate organizations — your prior remote home organization to all of the gadgets associated with the scaffold.
- Facebook Ads to Get Followers! - December 27, 2024
- ClickUp vs. Slack - December 20, 2024
- Mastering E-Commerce Analytics: A Blueprint for Success